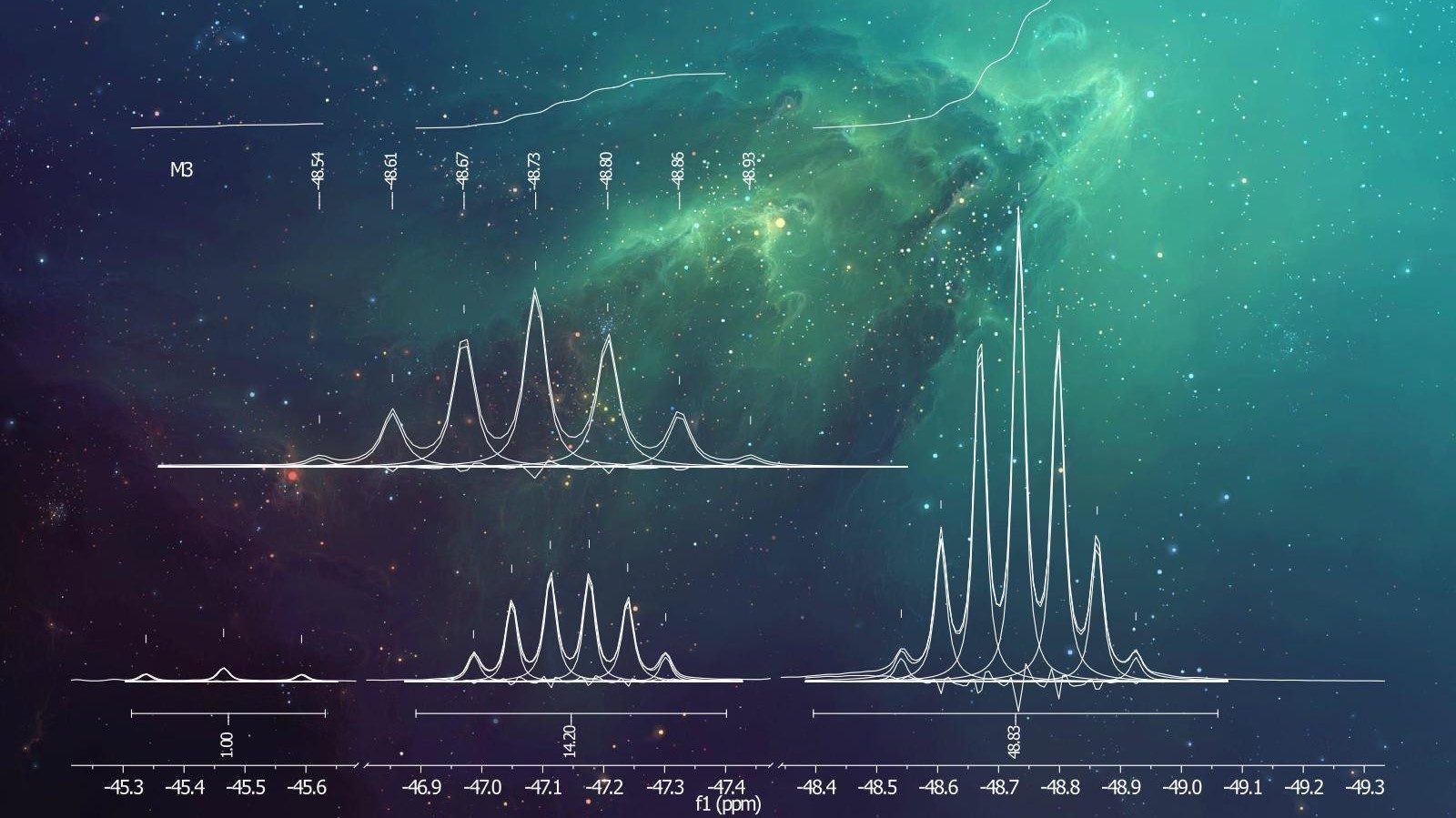
Rapid development of mass spectrometry allowed to apply it in countless fields. This course describes some of these applications - investigation of chemical reactions using mass spectrometry, hyphenated methods, in particular Ion Mobility Spectrometry (IMS), the use of photofragmentation and spectroscopy in combination with Mass Spectrometry, application of mass spectrometry to diagnose diseases, detection of explosives and drugs.
- Teacher: Aleksandr Pereverzev
- Teacher: Prof. Jana Roithova




